Introduction
Children's dental health is a crucial aspect of their overall well-being. Healthy teeth are not only important for chewing and speaking, but they also play a role in a child's self-esteem and social interactions. One of the key factors in maintaining good oral health is diet. What children drink can have a significant impact on their teeth, and diet soda has become a popular choice among young ones. This article aims to shed light on the potential dangers of diet soda, particularly focusing on its sugary and acidic components and their effects on children's teeth.
Understanding Diet Soda
Diet soda is a type of soft drink that is marketed as a healthier alternative to regular soda because it contains artificial sweeteners instead of sugar. Common ingredients in diet soda include artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose, and acids such as citric acid and phosphoric acid. Despite its "diet" label, diet soda is widely consumed by children and adolescents due to its sweet taste and the perception that it is a better option than sugary drinks.
The Role of Sugary Drinks in Dental Health
Sugary drinks are notorious for their role in tooth decay. When sugar is consumed, bacteria in the mouth feed on it and produce acids as a byproduct. These acids can erode the tooth enamel, leading to cavities. While diet soda contains little to no sugar, the misconception that it is a healthier choice can be misleading. It's important to compare the sugar content of regular soda with diet soda to understand that while diet soda may lack sugar, it still poses risks due to its acidity.
The Impact of Acidity on Teeth
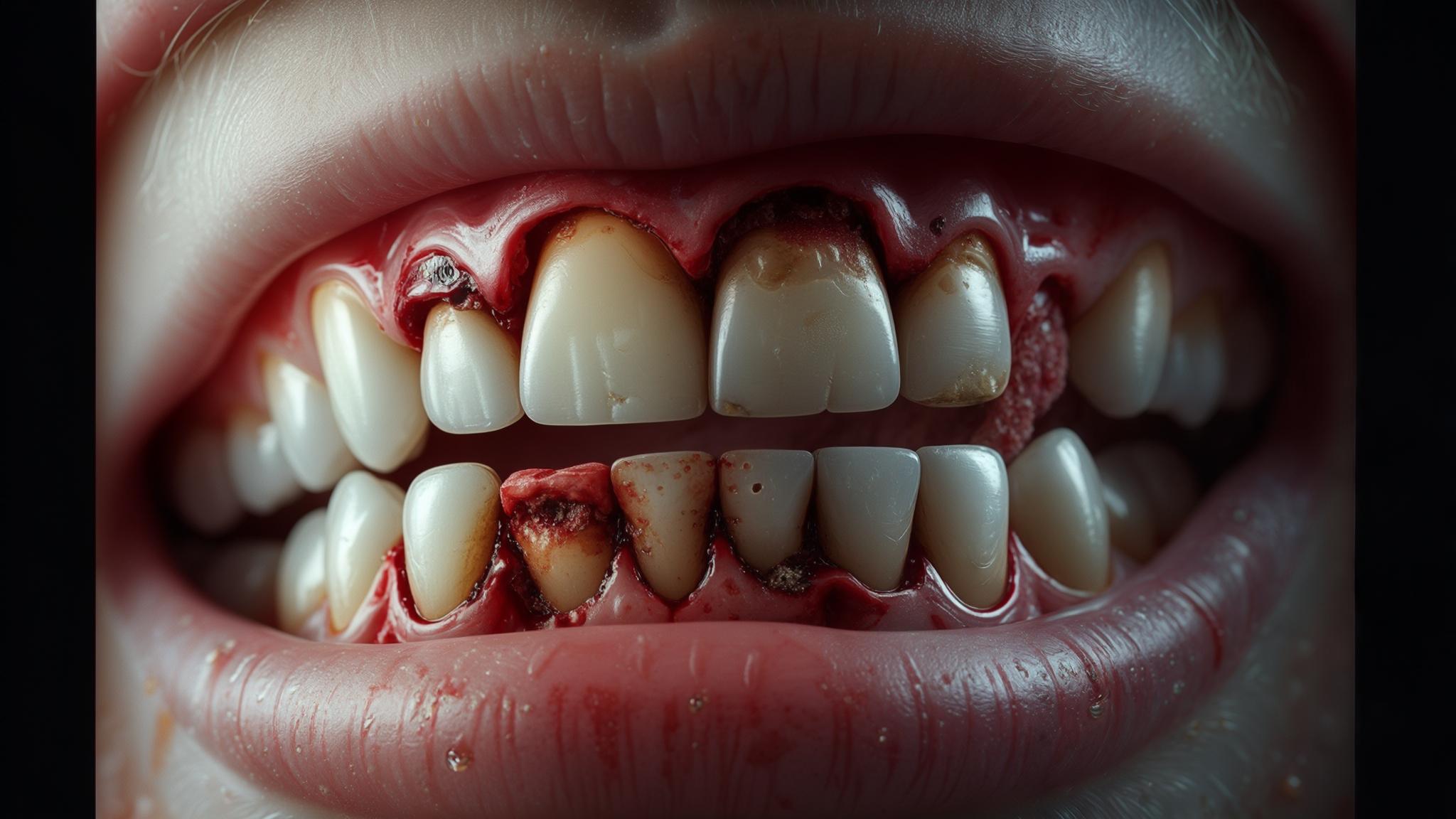
The pH level of a substance indicates its acidity, with lower pH values being more acidic. Tooth enamel is the hard, outer surface of the tooth that protects it from decay, but it is vulnerable to erosion from acidic substances. Common acids found in diet soda, like citric acid and phosphoric acid, can lower the pH in the mouth, leading to enamel erosion. Over time, this erosion can cause sensitivity, discoloration, and increased risk of cavities. Studies have shown a significant correlation between the consumption of acidic beverages and enamel erosion, highlighting the long-term effects on children's teeth.
Other Dental Health Concerns Related to Diet Soda
In addition to enamel erosion, diet soda can contribute to other dental health issues. It can cause dry mouth, which reduces saliva production. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids and washing away food particles. Without enough saliva, the risk of cavities increases. Furthermore, the artificial sweeteners and acids in diet soda can alter the oral microbiome, potentially leading to imbalances that affect overall dental health.
Recommendations for Parents
Parents can play a pivotal role in protecting their children's dental health by encouraging healthier beverage choices. Water and milk are excellent alternatives to diet soda. Regular dental check-ups are also crucial for monitoring oral health and catching any issues early. Teaching children about the effects of diet soda on their teeth can empower them to make better choices. Providing alternatives like flavored water or natural fruit juices can satisfy their taste buds without compromising their dental health.
Conclusion
In summary, while diet soda may seem like a harmless beverage choice, it poses several risks to children's dental health due to its acidic nature. Maintaining oral health through a balanced diet and proper dental care is essential. Parents are encouraged to be mindful of their children's beverage choices and to educate them about the potential dangers of diet soda.
References
- "Dental Erosion in Children Linked to Acidic Beverages," Journal of Pediatric Dentistry.
- "The Effects of Diet Soda on Oral Health," American Dental Association.
- "Understanding the Oral Microbiome," National Institutes of Health.